Main Finding: A Higher Proportion of Adult Patients in HRSA-Funded Health Centers Reported Ever Being Tested for HIV than the General Adult U.S. Population, Including across Major Racial/Ethnic Groups and Insurance Status
HIV testing is recommended for patients in all health-care settings, with patients able to opt-out of screening.1 HRSA-funded health centers are required to either offer HIV testing in some or all of their health center sites or refer patients to other health care providers for HIV tests.2
Data from the 2014 Health Center Patient Survey (HCPS) and the 2014 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) were used to examine the proportion of non-elderly adult patients (aged 18 – 64) who self-reported ever being tested for HIV. This brief compares the proportion of HCPS patients with the proportion of the general U.S. population that had been tested for HIV. NHIS is a nationally representative household survey and the data represent a national benchmark.
- Overall: A greater proportion of HCPS non-elderly adult patients reported ever being tested for HIV compared to the non-elderly adult NHIS population.
- Race/Ethnicity: Across the major racial/ethnic groups (including Whites, African Americans, and Hispanic/Latinos) a statistically significantly higher proportion of HCPS patients reported ever being been tested for HIV compared to the NHIS population.
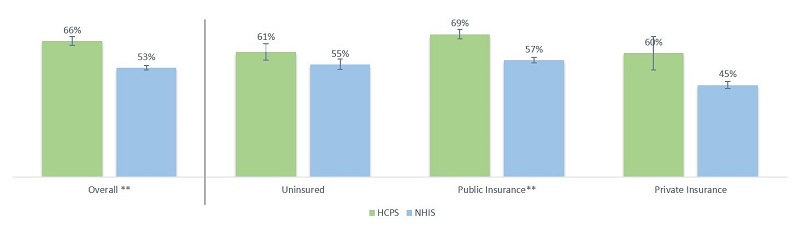
- Health Insurance: A statistically significant greater proportion of HCPS adult patients reported ever being tested for HIV when compared to similar NHIS publically insured non-elderly adults.
Exhibit 1: Proportion of HCPS and NHIS Non-Elderly Adults Aged 18 – 64 Who Had Ever Been Tested for HIV by Race/Ethnicity, 2014
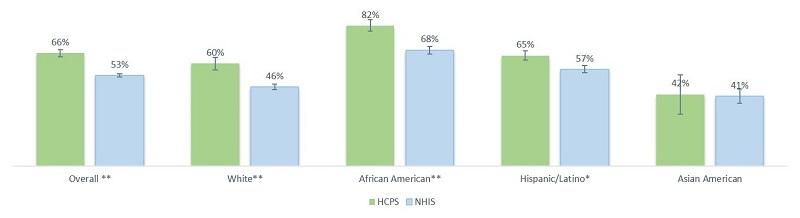
Exhibit 2: Proportion of HCPS and NHIS Non-Elderly Adults Aged 18 – 64 Who Had Ever Been Tested for HIV by Health Insurance Coverage, 2014
Statistically significant difference between HCPS and NHIS (* = p < 0.05 ** = p < 0.01)
1CDC, “Revised Recommendations for HIV Testing of Adults, Adolescents, and Pregnant Women in Health Care Settings,” Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, September 22, 2006. Accessed at http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5514a1.html.
2HHS, “HIV Testing in HRSA-Funded Health Center Sites,” Office of Inspector General, January 2013. Accessed at https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-06-10-00290.pdf (PDF - 1 MB)
Note: Sample populations were limited to HCPS and NHIS survey respondents that were 18 – 64 years old and had a family income under 200% of the federal poverty level. NHIS respondents were further limited to those that had two or more doctor’s office or health clinic visits in the last year, as the HCPS interviews patients that had a visit in the last year and are at the health center for their second visit.
Download a PDF version (PDF - 683 KB)